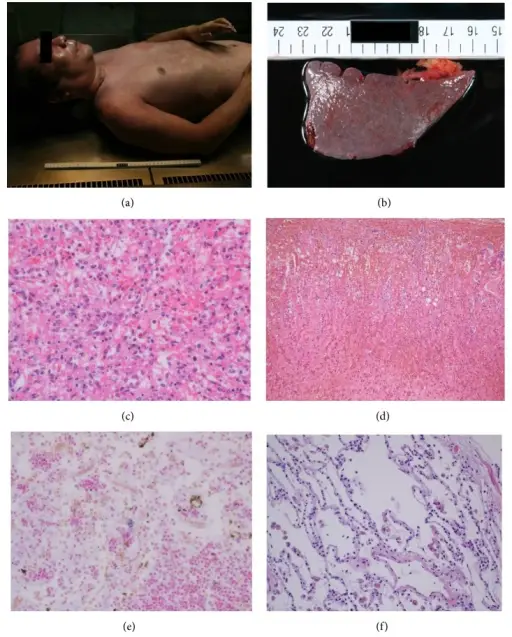
Nonspecific acute splenitis is the inflammation of the spleen that often is accompanied by enlargement of the spleen. Inflammation is due to micro-organisms or immune modulators such as cytokines that are unconfined as a response to antigens.
What is the Pathology of Nonspecific Acute Splenitis?
The pathology of nonspecific acute splenitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of nonspecific acute splenitis include viruses, bacterial, deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Acute or chronic infection (bacterial endocarditis, infectious mononucleosis, HIV, malaria, tuberculosis, histiocytosis, abscess).
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to nonspecific acute splenitis are infiltration of inflammatory cells, the proliferation of lymphoid follicles, congestion, and edema which is followed by propagation of fibrous tissues.
How does Nonspecific Acute Splenitis Present?
Patients with nonspecific acute splenitis typically there is no sex predilection is documented. Present at an age range of above 45-years-old, as the capsules of older spleens are thinner than their younger foils. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nonspecific acute splenitis include; splenic enlargement, congestion, and neutrophilic infiltration, which may occur in cases of sepsis due to the organisms themselves or secondary to inflammatory products.
How is Nonspecific Acute Splenitis Diagnosed?
Nonspecific acute splenitis is diagnosed by imaging studies including ultrasonography, noninvasive, highly sensitive aimed at evaluating splenic size. Angiographic findings to differentiate splenic cysts may also be utilized. Laboratory studies include a complete blood count (CBC) with differential, platelet count, and peripheral blood smear in cases of nonspecific acute splenitis.
How is Nonspecific Acute Splenitis Treated?
Nonspecific acute splenitis is treated through medical therapy which include antifungal treatment, parenteral broad-spectrum antibiotics, and corticosteroid therapy. Surgical interventions include percutaneous drainage and open drainage in case of an abscess develops.
What is the Prognosis of Nonspecific Acute Splenitis?
The prognosis of nonspecific acute splenitis is usually outstanding however, it is wedged by the underlying ailment causative state.