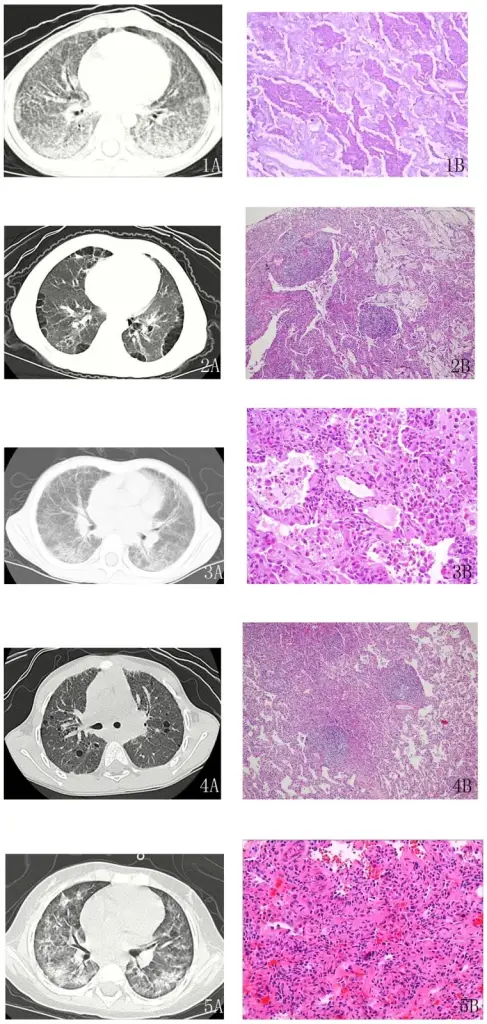
Chest tomography (CT) images and pathology results of several cases.1A: The CT shows a paving stone sign and air bronchograms in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (case 2 in Table 2). 1B: Under light microscopy, the case of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (case 2) shows evidence of periodic acid-Schiff-positive material filling the alveoli. Interstitial cell infiltrates, including lymphocytes and plasma cells with type II cell hyperplasia, are found. 2A: Multiple thin-walled cysts are seen in the subpleural region in the CT image of lipoid pneumonia (case 6). 2B: Light microscopy of lipoid pneumonia (case 6) shows a large amount of cholesterol crystallization in the alveolar spaces with lymphoid follicles in the alveolar septa. 3A: The CT image of non-specific interstitial pneumonia (case 15) shows reticulation on the background of ground glass opacity and interlobular septal thickening. 3B: A typical pathology picture of cellular non-specific interstitial pneumonia (case 15). The lungs are uniformly involved. Interstitial chronic inflammation consists of lymphocytes and plasma cells. 4A: On the background of ground glass opacity, thin-walled cysts are scattered in the lung fields (case 20, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia). 4B: In case 20, dense interstitial lymphoid infiltrates, including lymphocytes and plasma cells with type II cell hyperplasia, are observed. The alveolar septal interstitium is expanded by fibrosis. Lymphoid follicles are present. 5A: In case 24, a case of acute interstitial pneumonia, a patchy high-density shadow and bronchograms are seen in the CT image. 5B: Case 24 exhibits diffuse alveolar damage by light microscopy. The alveolar septal interstitium is expanded. Fibroblast proliferation and hyaline membrane disease are shown. Application of clinico-radiologic-pathologic diagnosis of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases in children in China. Xu D, Chen Z, Chen H, Huang R, Zhao S, Liu X, Zhou C, Peng Y, Yuan X, Zou J, Zhang H, Zhao D, Liu E, Zheng Y, Zhong L, Lu M, Lu J, Nong G - PloS one (2015). Not Altered. CC.
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia is an anomaly that could not be classified into one of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonia types.
What is the Pathology of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
The pathology of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is:
-Etiology: The cause of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is idiopathic, associated with systemic ailments and exposures to some drugs
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is unknown.
-Histology: The histology associated with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia shows a temporally unvarying interstitial course with fluctuating sizes to the fibrosis and interstitial inflammation.
How does Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Present?
Patients with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia typically have an insignificant female prevalence, present at age range of 46 and 55 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia include shortness of breath for some months, cough, weight loss, and fever.
How is Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Diagnosed?
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is diagnosed through transbronchial biopsy, a High-resolution CT scan to differentiate from usual interstitial pneumonia.
How is Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Treated?
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is treated medical care corticosteroid therapy and follow-up.
What is the Prognosis of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia?
The prognosis of nonspecific Interstitial pneumonia is good as many clients respond well to corticosteroid therapy.