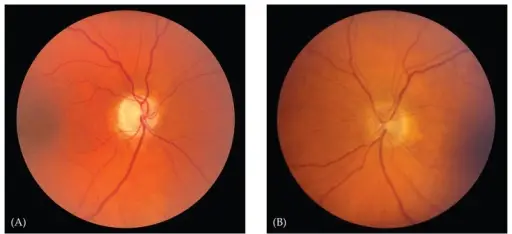
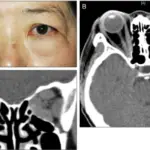
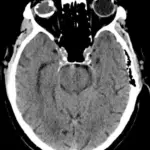
Optic neuritis is vision loss due to optic nerve demyelination. Optic neuritis is often seen in patients that have multiple sclerosis.
What is the Pathology of Optic Neuritis?
The pathology of optic neuritis is inflammatory demyelination of optic nerve caused by immune disease. Myelin is destroyed, exposing and causing the axon to poorly conduct impulses.
How does Optic Neuritis Present?
Optic neuritis presents with blurry vision or vision loss, eye pain, or color blindness.
How is Optic Neuritis Diagnosed?
Optic neuritis is diagnosed by an eye examination, color vision measurement, swinging flashlight test to check the afferent pupillary response, and optical coherence tomography.
How is Optic Neuritis Treated?
Optic neuritis is treated with administration of IV steroid, oral steroid, IV methylprednisolone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone.
What is the Prognosis of Optic Neuritis?
The prognosis of optic neuritis is visual recovery occurs within a month after treatment starts.