Palmoplantar keratoderma is an assorted group of ailments branded by persistent epidermal thickening to the palms and soles skin.
What is the Pathology of Palmoplantar Keratoderma?
The pathology of palmoplantar keratoderma is:
-Etiology: The cause of palmoplantar keratoderma is inherited or acquired allied to internal malignancy.
-Genes involved: AAGAB gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to palmoplantar keratoderma is unknown.
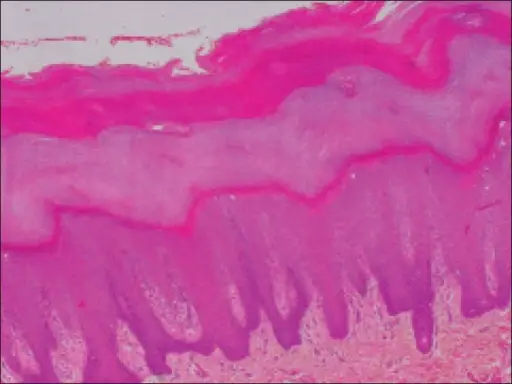
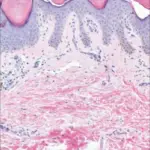
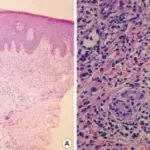
-Morphology: The morphology associated with palmoplantar keratoderma shows epidermal thickening to the palms and soles skin.
-Histology: Acanthosis.
How does Palmoplantar Keratoderma Present?
Patients with palmoplantar keratoderma typically have unknown prevalence The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with palmoplantar keratoderma include multiple hyperkeratotic papules, lesions on the palm and soles, pain pressure point.
How is Palmoplantar Keratoderma Diagnosed?
Palmoplantar keratoderma is diagnosed based on a grouping of clinical and histopathologic features and also genetic testing.
How is Palmoplantar Keratoderma Treated?
Palmoplantar keratoderma is treated through the management of the underlying conditions and stopping likely triggers.
What is the Prognosis of Palmoplantar Keratoderma?
The prognosis of palmoplantar keratoderma is good.