Pancreatoblastoma is a childhood tumor that is very rare of epithelial exocrine cells of the pancreas originate.
What is the Pathology of Pancreatoblastoma?
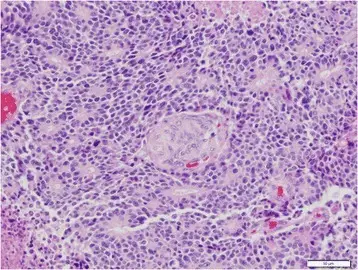
The pathology of pancreatoblastoma is: The study of fully malignant neoplasms, with a better rate than pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas characterized squamous islands admixed with undifferentiated cells.
-Etiology: The cause of pancreatoblastoma is is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pancreatoblastoma is not well understood.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with pancreatoblastoma shows large tumors up to 18cm in diameter.
-Histology: The histology associated with pancreatoblastoma shows squamous islands admixed with undifferentiated cells.
How does Pancreatoblastoma Present?
Patients with pancreatoblastoma typically have no gender prevalence present at an age range of 1 to 15 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pancreatoblastoma include abdominal mass, abdominal pain, jaundice, failure to thrive, abdominal distension, and endocrine syndromes.
How is Pancreatoblastoma Diagnosed?
Pancreatoblastoma is diagnosed through laboratory studies, raised serum levels of AFP. Radiological studies-MRI, CT scan, ultrasound, reveal large well-defined, multilobulated masses.
How is Pancreatoblastoma Treated?
Pancreatoblastoma is treated through complete surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy adjuvant.
What is the Prognosis of Pancreatoblastoma?
The prognosis of pancreatoblastoma is poor, with unresectable lesion and extensive metastasis.