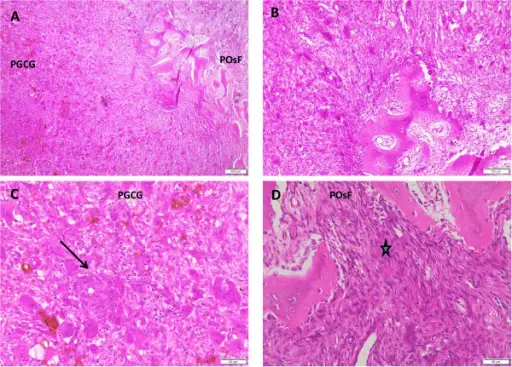
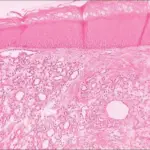
Peripheral ossifying fibroma is usually a fibroma of the gingiva which shows areas of calcification or ossification. It is a nonneoplastic enlargement of the gingiva.
-Etiology: The cause of peripheral ossifying fibromas is trauma.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to peripheral ossifying fibroma
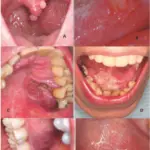
POF arises as an exophytic, ulcerated mass attached to the gingiva that shares similar clinical features with other extraosseous lesions.
-Histology: The histology associated with peripheral ossifying fibroma shows either ulcerated or intact stratified squamous epithelium.
How does Ossifying Fibroma Present?
Patients with ossifying fibroma typically affect females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ossifying fibroma include noticeable swelling and facial asymmetry.
How is Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Diagnosed?
Peripheral ossifying fibroma diagnosis is based on excisional biopsy.
How is Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Treated?
Peripheral ossifying fibroma is treated usually by surgical removal of the lesion down to the bone. If there are any adjacent teeth, they are cleaned thoroughly to remove any possible source of irritation.
What is the Prognosis of Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma?
The prognosis of peripheral ossifying fibroma is poor because the recurrence rate of the POF has been considered high for reactive lesions and it probably occurs due to incomplete initial removal, repeated injury, or persistence of the local irritants.