Pertussis bacterial infection also called whooping cough. It is a serious lung infection caused by bacteria and gets into the nose and throat.
What is the Pathology of Pertussis Bacterial Infection?
The pathology of pertussis bacterial infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of pertussis bacterial infection is Bordetella pertussis.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pertussis bacterial infection is when the bacteria is transmitted by aerosols and infects the ciliated epithelium of the airways, bacteria produces toxins in the respiratory tract which kills ciliated cells and causes their extrusion from the mucosa.
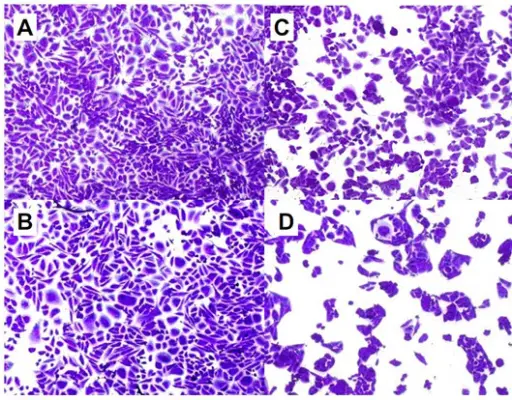
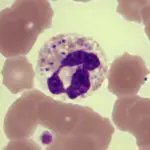
-Morphology: The morphology associated with pertussis bacterial infection shows small (approximately 0.8 μm by 0.4 μm), rod-shaped, coccoid, or ovoid Gram-negative bacterium that is encapsulated and does not produce spores. It is a strict aerobe. It is arranged singly or in small groups and is not easily distinguished from Haemophilus species.
-Histology: The histology associated with pertussis bacterial infection shows descending infection dominated by necrotizing bronchiolitis, intra-alveolar hemorrhage, and fibrinous edema.
How does Pertussis Bacterial Infection Present?
Patients with disease in lower case typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pertussis bacterial infection include exhaustion, Paroxysms, Vomiting.
How is Pertussis Bacterial Infection Diagnosed?
Pertussis bacterial infection is diagnosed by blood test, samples of mucus in the nose and throat.
How is Pertussis Bacterial Infection Treated?
Pertussis bacterial infection is treated by antibiotics.
What is the Prognosis of Pertussis Bacterial Infection?
The prognosis of pertussis bacterial infection is fair. The infection gradually resolves over weeks, but the coughing paroxysms can persist for several months.