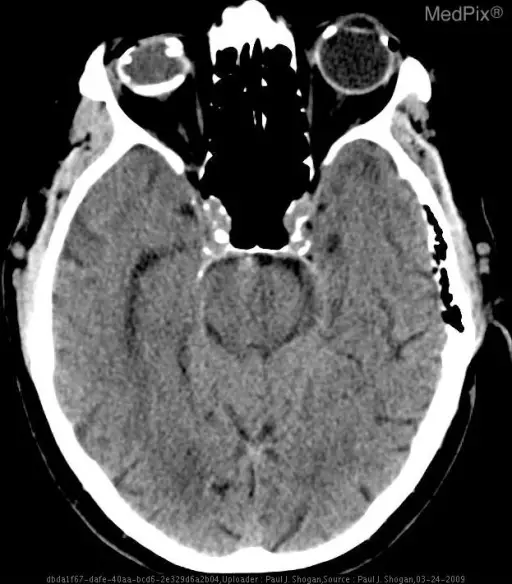
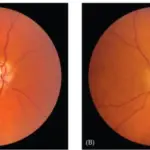
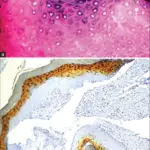
Phthisis bulbi is a clinical condition representing the end stage ocular response to eye diseases damage or injury causing scarring, inflammation, atrophy and eventually disorganization of the globe and the intraocular contents.
What is the Pathology of Phthisis Bulbi?
The pathology of phthisis bulbi is the proliferative reaction of a number of cells, internal disorganization, and inflammatory reaction.
How does Phthisis Bulbi Present?
Phthisis bulbi presents with intraocular inflammation, hypotony, microphthalmos, enophthalmos, and choroidal detachment.
How is Phthisis Bulbi Diagnosed?
Phthisis bulbi is diagnosed by physical examination, ocular history, and imaging tests.
How is Phthisis Bulbi Treated?
Phthisis bulbi is treated with administration of steroids, antibiotics, immune suppressing medications, and prosthesis.
What is the Prognosis of Phthisis Bulbi?
The prognosis of phthisis bulbi is curable in children with prompt treatment, but may lead to end stage eye if not treated.