Pineal gland pathology refers to any condition that may damage or alter the structure or function of the pineal gland.
What are Pinealomas?
Pinealomas are fairly uncommon type of brain tumor mostly encountered in childhood. The pineal gland is part of the epithalamus, a posterior segment of diencephalon, that secrets melatonin and is responsible for circadian rhythms. Pineal tumors and cysts may cause precocious puberty and delayed puberty.
What is the Pathology of Pinealomas?
The pathology of pinealomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of pinealomas is unknown. The tumor may be caused by genetic predisposition or environmental influence.
-Genes involved: Mutations to the RB1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: Proliferation of abberent germinal cells.
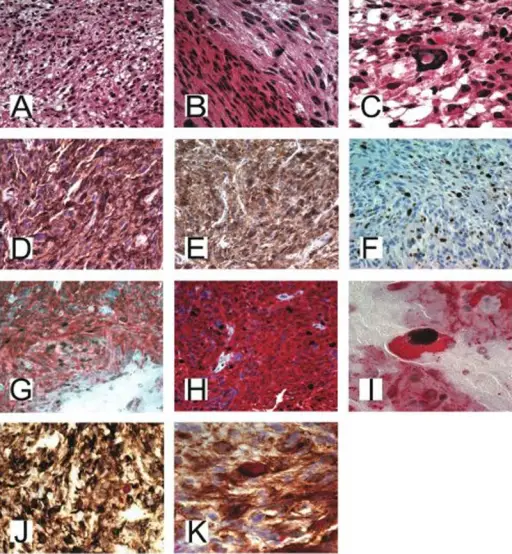
-Histology: The histology associated with pinealoma depends on which type of tumor that grows from pineocytoma.
How does Pinealoma Present?
Patients with a pinealoma typically could have this tumor also can cause hydrocephalus, gait disturbances or precocious puberty.
How is Pinealoma Diagnosed?
Pinealoma is diagnosed through several methods, which are central and peripheral vision assessment, opthalmosocpic assessment to check for optic nerve swelling which can signify increased intracranial pressure. Head MRI scans and CT scans to determine the size, shape, and location of the pinealoma. A biopsy allows determine the type and grade of the tumor.
How is Pinealoma Treated?
Surgical removal which may be followed by radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Pinealoma?
The prognosis of pinealoma depends on type and grade of tumor, patient`s age and gender and how the disease responds to treatment. The relative 5-year survival rate for pineal region tumors is 70%.
What are Pineoblastomas?
Pineoblastomas are an aggressive fast-growing, malignant type of cancer, that tend to invade nearby tissue within the brain and spine.
What is the Pathology of Pineoblastomas?
-Etiology: The cause of pineoblastomas is unknown, most occur sporadically, but some have been associated with certain genetic variants.
-Genes involved: Inherited genetic variants in either the RB1 gene or the DICER1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: Pineoblastomas originate from pinealocytes.
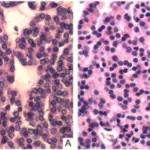
-Histology: The histology associated with pineoblastomas shows sheets of densely packed cells with undifferentiated cells that have minimal cytoplasm and large hyperchromatic nuclei. Necrosis, frequent mitotic figures, and nuclear molding may be present.
How do Pineoblastomas Present?
Patients with pineoblastomas have highest incidence is in childhood, particularly in children less than 2 years old. Because pineoblastomas block CSF flow many symptoms are related to CSF buildup such as headache, nausea, vomiting.
How are Pineoblastomas Diagnosed?
Pineoblastomas is diagnosed thought MRI, CT scanning, CSF puncture and biopsy.
How are Pineoblastomas Treated?
Pineoblastomas first-line therapy is aggressive surgical intervention. Pineoblastomas require postoperative radiotherapy to destroy remaining cancer cells or to slow their growth. Chemotherapy may also be used.
What is the Prognosis of Pineoblastomas?
The prognosis of pineoblastomas is poor, with a 5-year survival of 60%.
What are Pineocytomas?
Pineocytomas are rare pineal parenchymal tumor that is well differentiated.
What is the Pathology of Pineocytomas?
The pathology of pineocytomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of pineocytomas is unknown. No specific genetic alterations and also no identified risk factors have been found regarding pineocytomas.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: Aberrant cellular proliferation.
-Histology: Pinealcytomas is made up of cells in a uniform pattern that may form large pineocytomatous rosettes, pleomorphic cells with gangliocytic differentiation, or both.
How do Pineocytomas Present?
Patients with pineocytomas are typically females between 20 and 60 years old. Signs and symptoms include headache, ataxia, nausea, impaired vision, and loss of upward gaze.
How are Pineocytoma Diagnosed?
Pineocytoma is diagnosed by CT scanning, MRI and CSF. Confirmation of diagnosis is via brain biopsy.
How is Pineocytoma Treated?
Pineocytoma are treated by surgical excision. Some patients undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy, determined individually per patient.
What is the Prognosis of Pineocytoma?
The prognosis of pineocytoma is good. There is low recurrence rates with gross total resection.