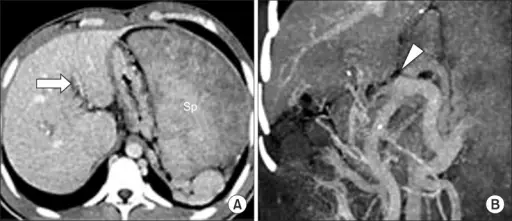
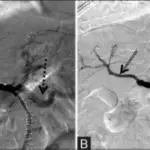
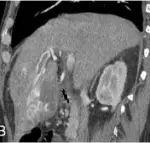
Portal vein obstruction is the blockage or narrowing of the portal vein by a blood clot.
What is the Pathology of Portal Vein Obstruction?
The pathology of portal vein obstruction is:
-Etiology: The cause of portal vein obstruction is prothrombotic disorders, tumor thrombus, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, various infections
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to portal vein obstruction hepatic artery buffer response allows for increased arterial flow to the liver when the portal vein is obstructed.
-Histology: The histology associated with portal vein obstruction no bridging fibrosis, can mimic cirrhosis.
How does Portal Vein Obstruction Present?
Patients with portal vein obstruction typically affect males present at the age range of 35-55. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with portal vein obstruction include abdominal pain, ascites (massive, intractable), portal hypertension, and bowel infarction.
How is Portal Vein Obstruction Diagnosed?
Portal vein obstruction is diagnosed via CT scan.
How is Portal Vein Obstruction Treated?
Portal vein obstruction is treated with anticoagulation medicine if caused by acute portal vein thrombosis.
What is the Prognosis of Portal Vein Obstruction?
The prognosis of portal vein obstruction is fair depending upon the cause.