Primary biliary cirrhosis is autoimmune in nature, that leads to progressive cholestasis and often end-stage liver disease.
What is the Pathology of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
The pathology of primary biliary cirrhosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of primary biliary cirrhosis is not clear.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to primary biliary cirrhosis includes a breakdown of immune tolerance to mitochondrial and nuclear antigens, causing injury to the biliary epithelial cells (BEC) lining the small intrahepatic bile ducts.
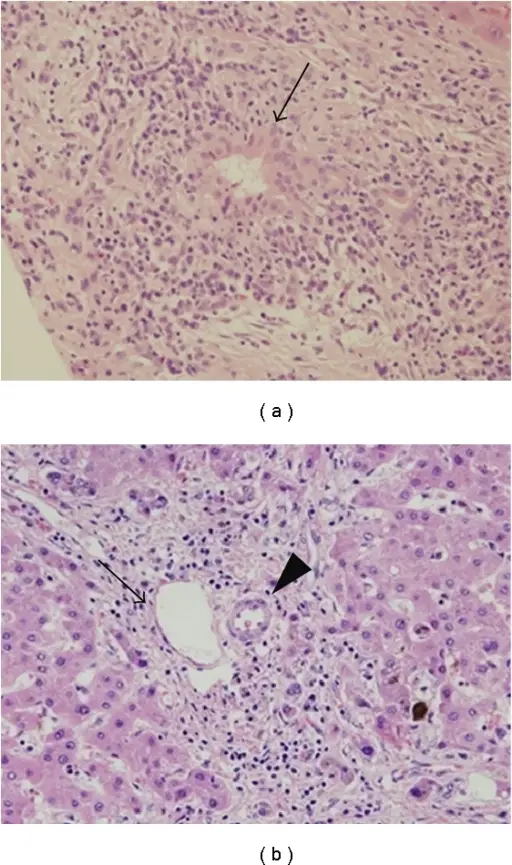
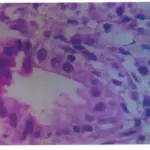
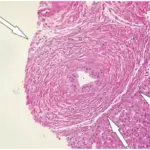
-Histology: The histology associated with primary biliary cirrhosis shows dense lymphocytic infiltrate in portal tracts with granulomatous destruction and loss of medium-sized interlobular bile ducts, focal and variable within the liver.
How does Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Present?
Patients with primary biliary cirrhosis typically affect females present at the age range of 35-60 The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with primary biliary cirrhosis include dry eyes and mouth, pain in the upper right abdomen, splenomegaly, musculoskeletal pain, edema, and ascites.
How is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Diagnosed?
Primary biliary cirrhosis is diagnosed using a blood test (AMA) and ultrasound.
How is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Treated?
Primary biliary cirrhosis is treated with ursodeoxycholic acid
What is the Prognosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
The prognosis of primary biliary cirrhosis is good with the symptoms free life up to 10 years.