Primary hepatolithiasis is the presence of gallstones in the biliary ducts of the liver.
What is the Pathology of Primary Hepatolithiasis?
The pathology of primary hepatolithiasis is:
-Etiology: The cause of primary hepatolithiasis is not clear, however, thought to be genetics, diets, and environmental causes.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to primary hepatolithiasis includes pigmented calcium bilirubin stones within dilated intrahepatic bile ducts featuring chronic inflammation, mural fibrosis, and proliferation of peribiliary glands, without extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
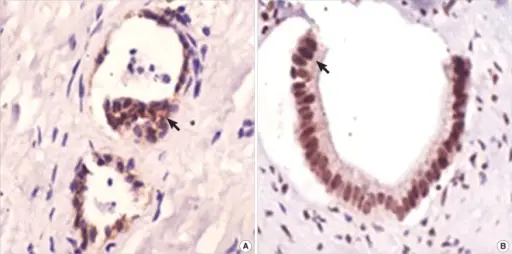
-Histology: The histology associated with primary hepatolithiasis shows the presence of calculi in the intrahepatic biliary tree and accompanying inflammation.
How does Primary Hepatolithiasis Present?
Patients with primary hepatolithiasis typically affect males and females present at the age range of 50-70. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with primary hepatolithiasis include abdominal pain, jaundice, and fever.
How is Primary Hepatolithiasis Diagnosed?
Primary hepatolithiasis is diagnosed using abdominal imaging.
How is Primary Hepatolithiasis Treated?
Primary hepatolithiasis is treated by doing surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Primary Hepatolithiasis?
The prognosis of primary hepatolithiasis is fair depending upon the cause.