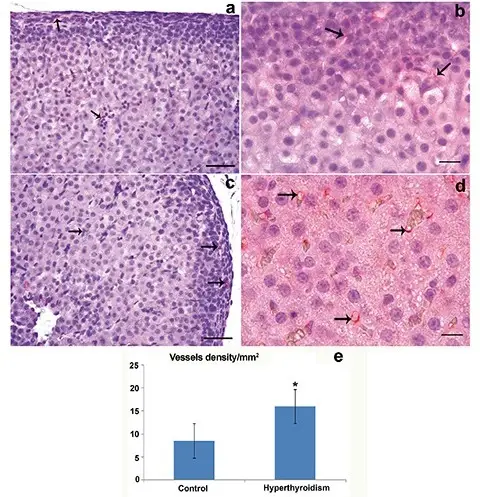
Primary hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is the source of abnormal thyroid hormone production.
What is the Pathology of Primary Hyperthyroidism?
The pathology of primary hyperthyroidism typically involves low TSH, high free T4, normal TRH stimulation test.
How does Primary Hyperthyroidism Present?
Patients with primary hyperthyroidism may present with cardiovascular issues such as tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, eyelid spasms, thyroidgoiters, and heat intolerance.
How is Primary Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Primary hyperthyroidism is typically diagnosed by a blood test to measure TSH level.
How is Primary Hyperthyroidism Treated?
Primary hyperthyroidism is typically treated by anti-thyroid drugs.
What is the Prognosis of Primary Hyperthyroidism?
The prognosis of primary hyperthyroidism is good with symptoms starting to resolve within several weeks.