Pseudo-gout is a form of arthritis that results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals.
What is the Pathology of Pseudogout?
The pathology of pseudo-gout is:
-Etiology: The cause of pseudogout is the deposits of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the joint.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pseudo-gout involves formation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystals in the cartilage of the synovial fluid.
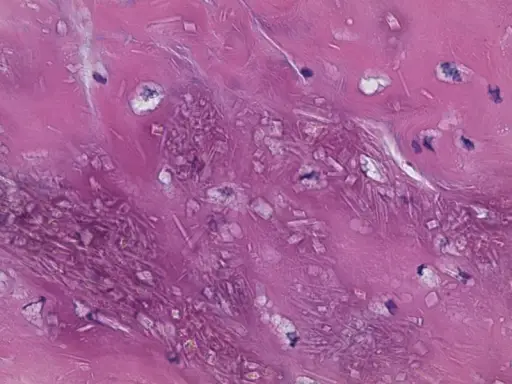
-Histology: The histology associated with pseudogout shows pale pink areas that may be surrounded by histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells. Rhomboid crystals may be appreciated.
How does Pseudogout Present?
Patients with pseudogout are typically over 60 years old, and are of any gender. The symptoms of pseudo-gout typically include swelling, pain, stiffness, and warmth in large joints.
How is Pseudogout Diagnosed?
Pseudo-gout is diagnosed by assessing the synovial fluid from the inflamed joint.
How is Pseudogout Treated?
Pseudo-gout is treated with NSAIDs and corticosteroids.
What is the Prognosis of Pseudogout?
The prognosis of pseudo-gout is very good in acute attacks. Acute attacks of pseudogout usually resolve within 10 days.