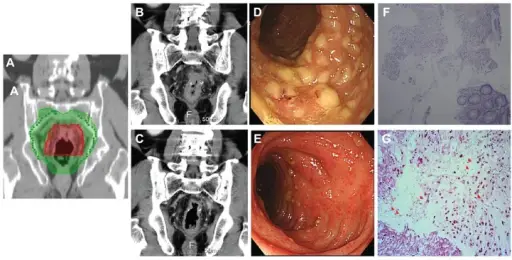
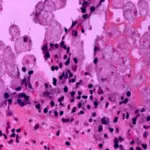
Pseudomembranous colitis is inflammation swelling, irritation of the large intestine. In many cases, it occurs after taking antibiotics. Using antibiotics can cause the bacterium Clostridium difficile C. diff to grow and infect the lining of the intestine, which produces the inflammation.
What is the Pathology of Pseudomembranous Colitis?
The pathology of pseudomembranous colitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of pseudomembranous colitis is antibiotics.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pseudomembranous colitis are: pathognomonic of infection by toxin-producing Clostridium difficile and develops as a result of altered normal microflora usually by antibiotic therapy that favors overgrowth and colonization of the intestine by Clostridium difficile and production of its toxins.
-Histology: The histology associated with pseudomembranous colitis shows whitish plaques attached to mucosa.
How does Pseudomembranous Colitis Present?
Patients with pseudomembranous colitis typically all genders at any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pseudomembranous colitis include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, pain or tenderness, fever, mucus in the stool, nausea, and dehydration.
How is Pseudomembranous Colitis Diagnosed?
Pseudomembranous colitis is diagnosed by examining a sample of feces in a laboratory to identify toxins produced by bacteria.
How is Pseudomembranous Colitis Treated?
Pseudomembranous colitis is treated by metronidazole, vancomycin, or fidaxomicin.
What is the Prognosis of Pseudomembranous Colitis?
The prognosis of pseudomembranous colitis is good. Most patients will experience complete recovery within 10 days.