Pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases is when collagen vascular diseases involve the lung to a slighter or more degree in their course.
What is the Pulmonary Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases?
The pathology of pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases is:
-Etiology: The cause of pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases are; rheumatoid arthritis systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, mixed connective tissue disease, and dermatomyositis-polymyositis.
-Genes involved: None.
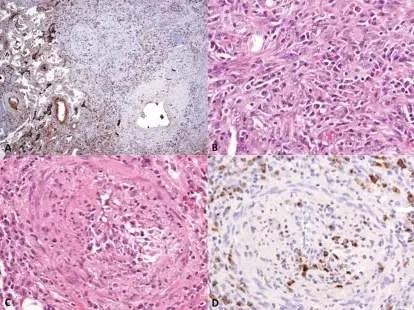
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases: Diffuse interstitial fibrosis pattern happens typically in scleroderma.
-Histology: The histology associated with pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases shows patchy, transient parenchymal infiltrates in lupus erythematosus.
How does Pulmonary Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases Present?
Patients with pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases typically, males more affected than females, present at the age range of 46 and 55 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia include shortness of breath for some months, cough, weight loss, and fever.
How is Pulmonary Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases Diagnosed?
Pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases is diagnosed through the diagnosis of ailment it presents in.
How is Pulmonary Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases Treated?
Pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases is treated through specific treatment of systemic autoimmune disease present.
What is the Prognosis of Pulmonary Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases?
The prognosis of pulmonary involvement in autoimmune diseases is poor.