Pyogenic osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone caused by an infecting organism.
What is the Pathology of Pyogenic Osteomyelitis?
The pathology of pyogenic osteomyelitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of pyogenic osteomyelitis is Staphylococcus aureus.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pyogenic osteomyelitis occurs both by direct routes and by hematogenous spread from an infection of the skin, urogenital tract, lung, or upper respiratory tract.
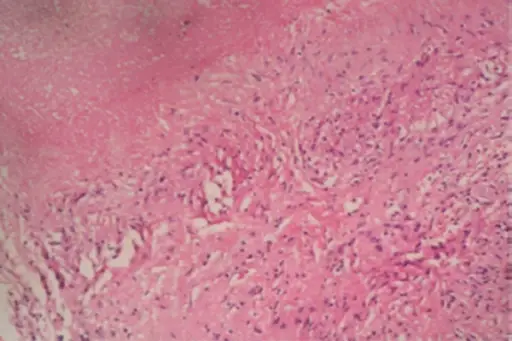
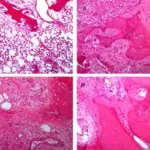
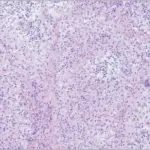
-Histology: The histology associated with pyogenic osteomyelitis shows neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells with bone necrosis and reactive new bone formation.
How does Pyogenic Osteomyelitis Present?
Patients with pyogenic osteomyelitis typically affect males more than females both young and old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pyogenic osteomyelitis include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, weakness, and inability to walk especially in children with acute bacterial osteomyelitis.
How is Pyogenic Osteomyelitis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pyogenic osteomyelitis is through radiographs, MRI, and CT scans.
How is Pyogenic Osteomyelitis Treated?
Pyogenic osteomyelitis is treated by prolonged antibiotic therapy for weeks or months.
What is the Prognosis of Pyogenic Osteomyelitis?
The prognosis of pyogenic osteomyelitis is good with aggressive treatment however, there is a chance of recurrence of the infection.