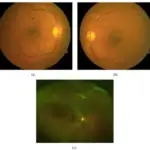
(a) Fundus photograph of the left eye shows central retinal vein occlusion with disk edema, dilated retinal veins, peripapillary cotton-wool spots, and hemorrhages. (b) Fluorescein angiogram (1 minute and 14 seconds after injection of the dye) photograph of the left eye shows central retinal vein occlusion with marked delay in arteriovenous transit time, masked by retinal hemorrhages, vessel wall staining, and a few small patches of retinal capillary obliteration. (c) Fundus photography of the left eye after 8 weeks shows that superficial cotton-wool spots and retinal hemorrhages were all resolved.A Rare Cause of Unilateral Central Retinal Vein Occlusion in a Young Patient: Type III Mixed Cryoglobulinemia. Doguizi S, Sekeroglu MA, Anayol MA, Yilmazbas P - Case reports in ophthalmological medicine (2016). Not Altered. CC
Radiation vasculitis is an inflammatory condition of blood vessels induced by exposure to radiation treatment of another medical condition.
What is the Pathology of Radiation Vasculitis?
The pathology of radiation vasculitis is irritation of smooth muscle, endothelial and immune cells.
How does Radiation Vasculitis Present?
Radiation vasculitis presents with ischemia, ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, and dizziness.
How is Radiation Vasculitis Diagnosed?
Radiation vasculitis is diagnosed by physical examination, medical history, magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography (CT) angiography.
How is Radiation VasculitisTreated?
Radiation vasculitis is treated with medications such as aspirin.
What is the Prognosis of Radiation Vasculitis?
The prognosis of radiation vasculitis is good.