Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is a disease of the glomeruli characterized by rapid loss of function of the kidney.
What is the Pathology of Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis?
The pathology of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is infections, multisystemic disease, drugs and toxic agents.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, the antigen formed against the GBM antibodies lead to increased damage to the kidney.
-Morphology: Not applicable.
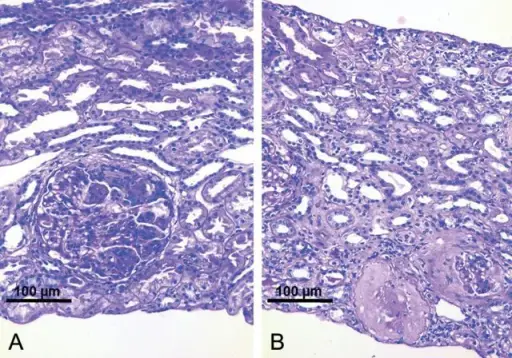
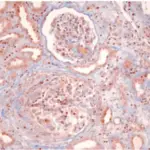
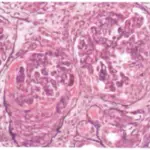
-Histology: The histology associated with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis shows crescentic formation, fibrinoid necrosis, focal breakage of the glomerular basement membrane, necrotizing lesions,
How does Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis Present?
Patients with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis typically both male and female present at the age range of 20-30 years the first peak and 60-70 years the second peak. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis include oliguria, anuria, fever, myalgia, haemoptysis, anemia.
How is Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis Diagnosed?
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is diagnosed with history taking , urinalysis, serologic tests, renal biopsy.
How is Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis Treated?
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is treated with plasmapheresis, corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide.
What is the Prognosis of Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis?
The prognosis of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is poor.