Renal papillary adenoma is benign renal tumors rising from the renal tubular epithelium usually situated within the cortex.
What is the Pathology of Renal Papillary Adenoma?
The pathology of renal papillary adenoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of renal papillary adenoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to renal papillary adenoma unknown.
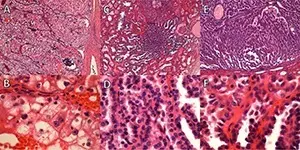
-Morphology: The morphology associated with renal papillary adenoma shows small, pale yellow-gray, discrete, well-circumscribed nodules.
-Histology: The histology associated with renal papillary adenoma shows complex, branching, papillomatous structure. Cuboidal to polygonal shaped cells with regular, small central nuclei, scanty cytoplasm, and no atypia may be seen.
How does Renal Papillary Adenoma Present?
Patients with renal papillary adenoma typically have no gender preference present at the age range of 70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with renal papillary adenoma include, most are asymptomatic.
How is Renal Papillary Adenoma Diagnosed?
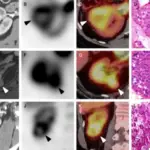
Renal papillary adenoma is diagnosed through kidney biopsy and CT scan imaging.
How is Renal Papillary Adenoma Treated?
Renal papillary adenoma is treated through observation and cryoablation.
What is the Prognosis of Renal Papillary Adenoma?
The prognosis of renal papillary adenoma is good. Have no metastatic potential.