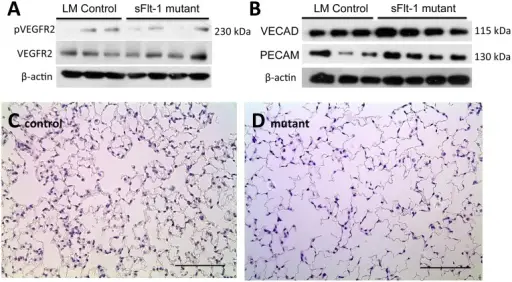
Mesenchymal VEGF sequestration does not affect pulmonary angiogenesis but affects acinar air space morphogenesis.Western blot analyses of (A) total VEGFR-2 and phosphorylated VEGFR-2, and (B) endothelial markers PECAM-1 and VE-cad. No significant difference in expression between control and mutant mice was noted on either analysis. (C-D) Representative H&E images of peripheral lung sections from control and mutant mice demonstrate larger acinar air spaces in mutants. This was confirmed by mean linear intercept analysis. Images at 20x magnification, scale bars represent 100 μm. Sequestration of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Induces Late Restrictive Lung Disease. Wieck MM, Spurrier RG, Levin DE, Mojica SG, Hiatt MJ, Reddy R, Hou X, Navarro S, Lee J, Lundin A, Driscoll B, Grikscheit TC - PloS one (2016). Not Altered. CC.
Restrictive lung disease is a diverse category of lung ailments producing similar inflammatory and fibrotic changes in the interstitium or interalveolar septa of the lung. Characterized by decreased total lung capacity and reduced expansion of lung parenchyma.
Examples of restrictive lung disease include:
- Fibrosing diseases
- Granulomatous diseases
- Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- Pulmonary eosinophilia
- Pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Smoking-related interstitial diseases
- Surfactant dysfunction disorders