Retinal vein occlusion is a vascular disease characterized by the engorgement and dilation of retinal veins.
What is the Pathology of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The pathology of retinal vein occlusion is obstruction of retina veins lumen causing a restricted blood flow.
How does Retinal Vein Occlusion Present?
Retinal vein occlusion presents with dark spots, lines floating in vision, pain and pressure in the eye.
How is Retinal Vein Occlusion Diagnosed?
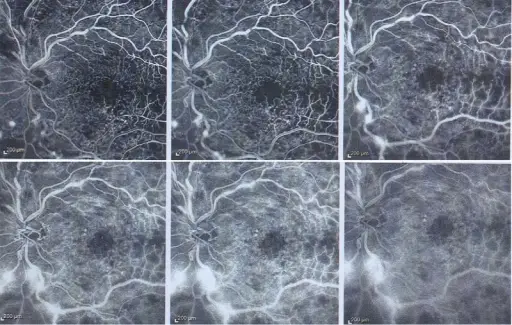
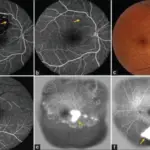
Retinal vein occlusion is diagnosed by fluorescein angiography.
How is Retinal Vein Occlusion Treated?
Retinal vein occlusion is treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor, focal laser therapy, laser surgery, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and sublingual isosorbide dinitrate.
What is the Prognosis of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The prognosis of retinal vein occlusion is fair. Vision may be restored in some patients, while some may not see improvements.