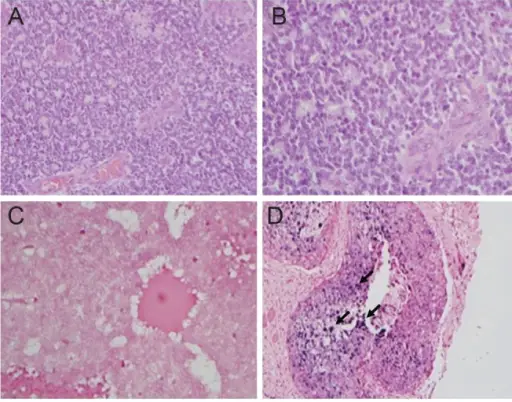
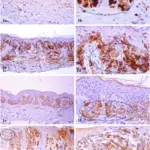
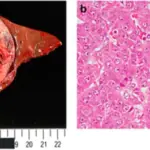
Retinoblastoma is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the retina.
What is the Pathology of Retinoblastoma?
The pathology of retinoblastoma is:
–Etiology: The cause of retinoblastoma is a genetic mutation.
–Genes involved: RB1 gene
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to retinoblastoma involves inactivation of RB1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene. Normally, RB1 gene is necessary for the normal differentiation and growth of retinal stem cells and its mutation results in unregulated growth of these cells and development of the tumor.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with retinoblastoma is leukocoria, a white pupillary reflex.
How does Retinoblastoma Present?
Patients with retinoblastoma are typically infant males. The average age of diagnosis of retinoblastoma is 2. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with retinoblastoma include an unusual white reflection in the pupil, squint, change of iris color, poor vision.
How is Retinoblastoma Diagnosed?
Retinoblastoma is diagnosed by electroretinogram, which measures the electrical activity of the retina, MRI of the eyes, eye sockets, and brain to check any other tumors.
How is Retinoblastoma Treated?
Retinoblastoma is treated by systemic chemotherapy followed by surgery and high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
What is the Prognosis of Retinoblastoma?
The prognosis of retinoblastoma is good. Retinoblastoma is almost always curable, especially if it hasn’t spread beyond the eye. Child will have frequent checkups to watch for signs that the cancer has come back.