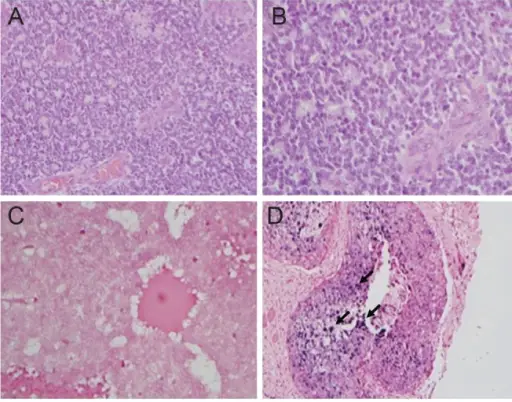
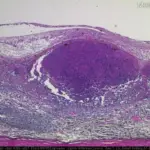
Retinoblastoma is eye cancer that originates from the retina.
What is the Pathology of Retinoblastoma?
The pathology of retinoblastoma is mutational inactivation of both alleles of RB1 gene mapping to chromosome 13q14 and encodes retinoblastoma protein acting as tumor suppressor.
How does Retinoblastoma Present?
Retinoblastoma typically presents in affected children with light induced white coloration of the pupil, different directional eye focus, redness, and swelling of the eye.
How is Retinoblastoma Diagnosed?
Retinoblastoma is diagnosed by eye examination, ultrasound image test, CT scan, MRI.
How is Retinoblastoma Treated?
Retinoblastoma is treated with intra-arterial chemotherapy, intravitreal chemotherapy, laser therapy, cryotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Retinoblastoma?
The prognosis of retinoblastoma is fair.