Retinopathy of prematurity is a potentially blinding eye disorder that primarily affects premature infants weighing about 3 pounds or less that are born before 31 weeks of gestation.
What is the Pathology of Retinopathy of Prematurity?
The pathology of retinopathy of prematurity is:
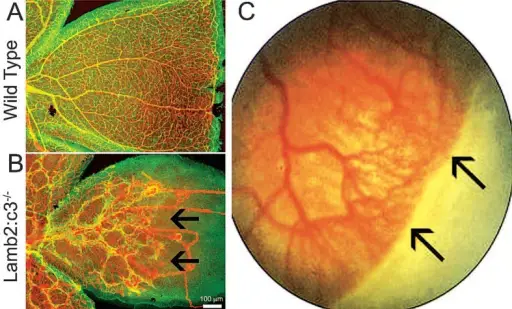
–Etiology: The cause of retinopathy of prematurity is when abnormal blood vessels grow and spread throughout the retina, the tissue that lines the back of the eye. These abnormal blood vessels are fragile and can leak, which can scar the retina and pull the retina out of position.
–Genes involved: Genes for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), the Wnt signaling pathway, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), inflammatory mediators, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to retinopathy of prematurity are delayed retinal vascular growth after premature birth followed by hypoxia induced neoangiogenesis (new blood vessel growth) on the retina.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with retinopathy of prematurity include abnormal blood vessels which are weak and fragile that grow and spread throughout the retina.
How does Retinopathy of Prematurity Present?
Patients with retinopathy of prematurity have no significant difference between gender. Premature babies born before 31 weeks gestation and less than 3 pounds are at increased risk. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with retinopathy of prematurity are very subtle, an ophthalmologist is needed to recognize the features of the disease.
How is Retinopathy of Prematurity Diagnosed?
Retinopathy of prematurity is diagnosed by ophthalmoscopy which examines the internal structures of the eyes, specifically checking for abnormality of the retinas. In this process the pupils are dilated by eyedrops to study the retinas which may show a line of demarcation and a ridge and proliferation of retinal vessels if retinopathy of prematurity is present.
How is Retinopathy of Prematurity Treated?
Retinopathy of prematurity is treated by laser therapy which burns away the area around the edge of the retina with abnormal blood vessels. Bevacizumab may help to stop the progression because it is antivascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody.
What is the Prognosis of Retinopathy of Prematurity?
The prognosis of retinopathy of prematurity is excellent because it may resolve without treatment, and may resolve without damage. In mild cases the abnormal retinal blood vessels may heal on their own within the first four months of life.