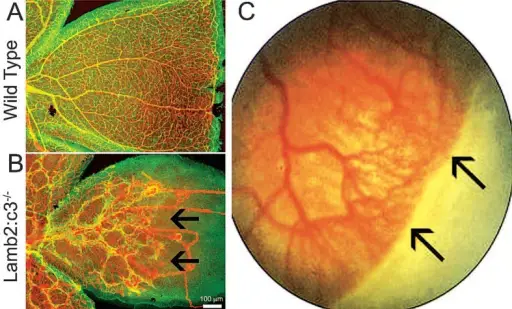
Vascular growth in peripheral retina is affected in laminin s as well as infants with retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). *(A) Postnatal day 15 wild type retina was immunostained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (green) to label astrocytes and CD31 (Red) to label blood vessels. *(B) Postnatal day 15 Lamb2:c3 retina was immunostained for GFAP (green) to label astrocytes and CD31 (Red) to label blood vessels. Notice abnormal astrocyte patterning and vascular growth. Astrocyte patterning and subsequent vascular growth was affected in the peripheral retina (black arrows). **(C) Black arrows at the peripheral retina show no vascular growth in an infant with ROP. *[Data in A and B are from the author’s laboratory]. **[Reprinted by permission from Nature Publishing Group. Gariano and Gardner, 2005. Originally published in Nature; 438:960-966.]3. The cell-matrix interface: a possible target for treating retinal vascular related pathologies. Gnanaguru G, Brunken WJ - Journal of ophthalmic & vision research (2012). Not Altered. CC.
Retinopathy of prematurity is a potential blindness disorder primarily affecting prematurely born infants.
What is the Pathology of Retinopathy of Prematurity?
The pathology of retinopathy of prematurity is incomplete outward growth of the blood vessels from the central part of the retina.
How does Retinopathy of Prematurity Present?
Retinopathy of prematurity presents with birth weight less than 1.5kg, tortuosity of vessels.
How is Retinopathy of Prematurity Diagnosed?
Retinopathy of prematurity is diagnosed by dilated fundus examination with scleral depression.
How is Retinopathy of Prematurity Treated?
Retinopathy of prematurity is treated with oral propranolol, intravitreal injection of bevacizumab, scleral buckling, vitrectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Retinopathy of Prematurity?
The prognosis of retinopathy of prematurity is fair, but it can progress to a more severe state with improper or no treatment.