Rheumatic heart disease is an inflammatory disease that follows an S. pyogenes infection.
What is the Pathology of Rheumatic Heart Disease?
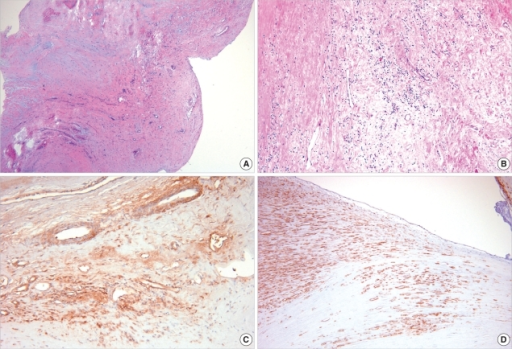
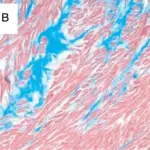
Rheumatic heart disease pathology involves the cardiac valves, commonly affecting the mitral valve causing leaflet thickening and fibrosis leading to stenosis or regurgitation. Thrombotic vegetation is seen in acute phases while in chronic, fused commissures, valve thickening and calcification is observed.
How does Rheumatic Heart Disease Present?
Rheumatic heart disease presentation involves the heart, joints, CNS, subcutaneous and skin. Fever, swollen joints, nodules, rashes, chest discomfort, and weakness may be noted.
How is Rheumatic Heart Disease Diagnosed?
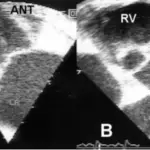
Rheumatic heart disease is diagnosed with 2D echo, electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, MRI and blood tests.
How is Rheumatic Heart Disease Treated?
Rheumatic heart disease treatment includes preventing the disease by properly treating strep infections. Treatment of advanced damage is surgical repair/replacement of the affected valve.
What is the Prognosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease?
The prognosis of rheumatic heart disease is poor due to possible progression after repair.