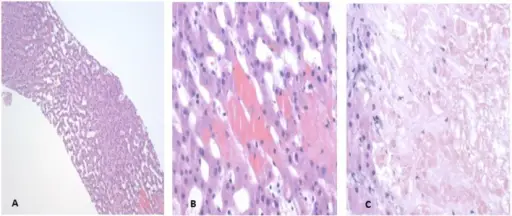
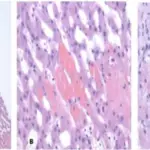
Right-sided heart failure or cor pulmonale is often caused by a left sided heart failure, causing blood to flow back to the lungs due to weakened left ventricle.
What is the Pathology of Right-Sided Heart Failure?
Right sided heart failure is due to impaired contractility caused by pressure, volume overload or contractile dysfunction.
How is Right-Sided Heart Failure?
Right sided heart failure presents as shortness of breath that awakens patients at night and during exercise or when lying flat, edema of the legs, ankles or feet, and abdominal distention.
How is Right-Sided Heart Failure Diagnosed?
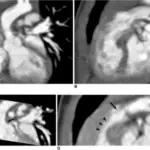
Right sided heart failure diagnosis is based on blood tests, CT scan, chest x-ray, cardiac catheterization, coronary angiography, electrocardiogram, 2D and echo.
How is Right-Sided Heart Failure Treated?
Treatment for right sided heart failure is symptomatic, and drugs such as diuretics, beta blockers, pulmonary vasodilators, digoxin, and vasodilators may be used. Lifestyle changes are also essential and surgical procedures such as ventricular assist device (VAD) surgery and heart transplant may be done in advanced cases.
What is the Prognosis of Right-Sided Heart Failure?
Right sided heart failure prognosis is poor with a five-year survival rate of 47% and 2-year mortality of 25%.