Sarcoidosis is a systemic ailment of mysterious cause characterized by noncaseating granulomas in several tissues and organs.
What is the Pathology of Sarcoidosis?
The pathology of sarcoidosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown.
-Genes involved: HLA genotypes (class I HLA-A1 and HLA-B8).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sarcoidosis is not fully understood, some evidence proposes that it is an illness of disordered immune regulation in genetically susceptible persons exposed to certain agents.
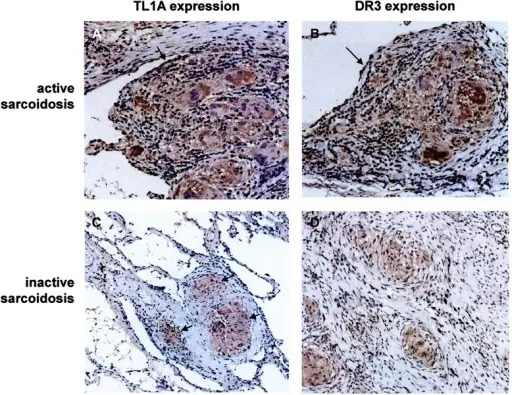
-Histology: The histology associated with sarcoidosis shows lesions that are disseminated along the lymphatics, around the bronchi, and blood vessels.
How does Sarcoidosis Present?
Patients with sarcoidosis typically male-to-female ratio is roughly 1:2. present at age range of 25-35 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sarcoidosis include the onset of shortness of breath, cough, chest pain, hemoptysis, fever, fatigue, weight loss, anorexia, night sweats.
How is Sarcoidosis Diagnosed?
Sarcoidosis is diagnosed through laboratory Studies- Serum markers of sarcoidosis (sIL-2R), (SAA) (ACE). Imaging Studies-Chest radiograph and High-resolution CT scan detect fibrosis and active alveolitis.
How is Sarcoidosis Treated?
Sarcoidosis is treated through medical care- steroid treatment and surgical care lung transplantation.
What is the Prognosis of Sarcoidosis?
The prognosis of sarcoidosis is good with 65% to 70% of affected patients recovering with minimal or no residual manifestations.