Scabies is a pruritic skin infestation caused by the host-specific mite Sarcoptes scabiei hominis.
What is the Pathology of Scabies?
The pathology of scabies is:
-Etiology: The cause of scabies is the mite Sarcoptes scabiei hominis.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to scabies, caused by a mite. Mite does not penetrate more than stratum corneum layer. Transmission is by direct skin-to-skin contact.
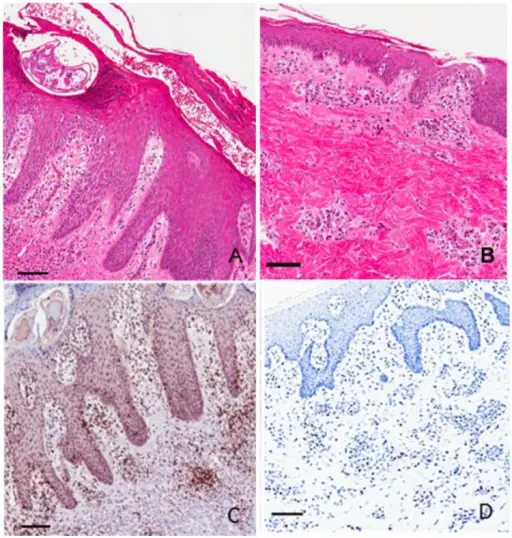
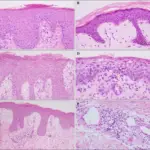
-Morphology: The morphology associated with scabies shows nodular scabies, mites, ova, larvae, feces when burrow is executed.
-Histology: The histology associated with scabies shows dermal infiltrate by histiocytes, mast cells lymphocytes, and eosinophils.
How does Scabies Present?
Patients with scabies are typically more common in females present at the age range of 18 years and below. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with scabies include rubbing and scratching grayish, threadlike elevations, erythematous vesicles, and papules.
How is Scabies Diagnosed?
Scabies is diagnosed is made clinically through history and physical examination, biopsy to rule out other dermatoses.
How is Scabies Treated?
Scabies is treated through medical therapy scabicidal agent (permethrin), antimicrobial agent, and proper hygiene for prevention.
What is the Prognosis of Scabies?
The prognosis of scabies is good owing to proper treatment and diagnosis with rare complications.