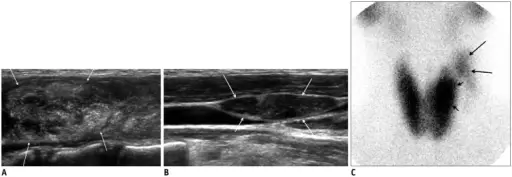
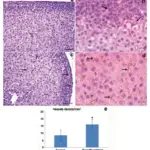
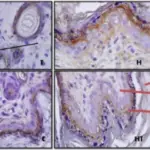
Secondary Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is stimulated by excessive thyroid-stimulating hormone.
What is the Pathology of Secondary Hyperthyroidism?
The pathology of secondary hyperthyroidism typically involves high TSH, and/or abnormal.
How does Secondary Hyperthyroidism Present?
Secondary hyperthyroidism typically presents with nervousness, weight loss, sweating, palpitations, tremor, diarrhea, heat intolerance, fatigue, loss of libido, and oligomenorrhea.
How is Secondary Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Secondary hyperthyroidism is typically diagnosed by a blood test to measure TSH level.
How is Secondary Hyperthyroidism Treated?
Secondary hyperthyroidism is typically treated with antithyroid medications or thyroid surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Secondary Hyperthyroidism?
The prognosis of secondary hyperthyroidism is good with symptoms starting to resolve within several weeks.