Sialadenitis is an infection or inflammation of the salivary glands.
What is the Pathology of Sialadenitis?
The pathology of sialadenitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of sialadenitis is most commonly by sialolithiasis, bacterial or viral infections.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sialadenitis involves inflammation of the salivary glands.
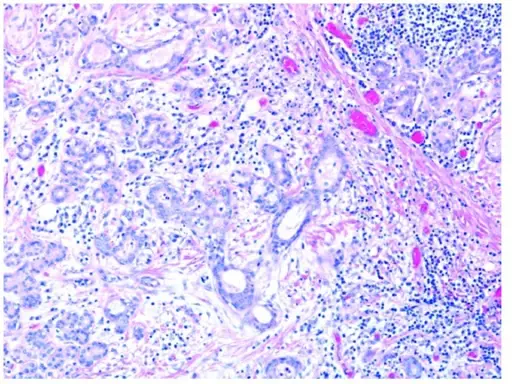
-Histology: The histology associated with sialadenitis shows stones that are readily visualized as high attenuating masses. There may be edema, hyperemia, and acute inflammation with dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.
How does Sialadenitis Present?
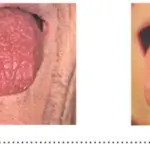
Patients with sialadenitis are typically males of varying age ranges. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sialadenitis include pain and swelling.
How is Sialadenitis Diagnosed?
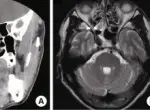
Sialadenitis is diagnosed by physical exam, and biopsy.
How is Sialadenitis Treated?
Sialadenitis is treated by antimicrobial therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Sialadenitis?
The prognosis of sialadenitis is very good.