Sickle cell nephropathy is the kidney manifestation of the complication of sickle cell disease.
What is the Pathology of Sickle Cell Nephropathy?
The pathology of sickle cell nephropathy is:
-Etiology: The cause of Sickle cell nephropathy is occluded vessels (vasa recta) in sickle cell disease.
-Genes involved: SCD.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sickle cell nephropathy results from occluded vessels due to sickle red blood cells.
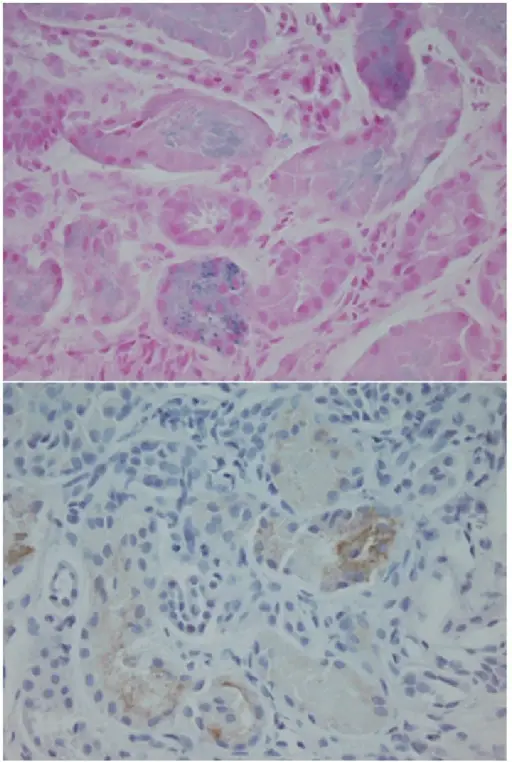
-Morphology: The morphology associated with sickle cell nephropathy shows glomerular hypertrophy, papillary necrosis.
-Histology: The histology associated with sickle cell nephropathy shows abundant hemosiderin granules in proximal tubular epithelial cells.
How does Sickle Cell Nephropathy Present?
Patients with sickle cell nephropathy typically have more females present at the age range of any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Sickle cell nephropathy include proteinuria, painful gross hematuria, glomerular hyperfiltration, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fevers.
How is Sickle Cell Nephropathy Diagnosed?
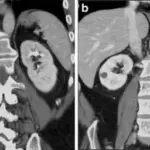
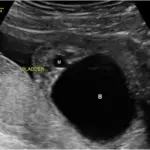
Sickle cell nephropathy is diagnosed by clinical presentation, laboratory works including CBC count, urinalysis, basic metabolic panel. Imaging studies such as renal ultrasound, CT scan, and renal biopsy.
How is Sickle Cell Nephropathy Treated?
Sickle cell nephropathy is treated symptomatic medical management and surgical care kidney transplant.
What is the Prognosis of Sickle Cell Nephropathy?
The prognosis of sickle cell nephropathy is good, with proper management of the underlying cause.