Sinusitis is condition characterized by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses lining.
What is the Pathology of Sinusitis?
The pathology of sinusitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of sinusitis is acute or chronic rhinitis, an extension of a periapical infection through the bony floor of the sinus in case of maxilla sinusitis.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sinusitis is an inflammatory response.
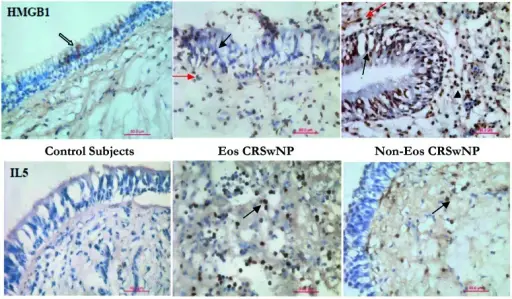
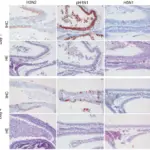
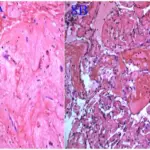
-Histology: The histology associated with sinusitis shows there are numerous neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and some eosinophils with abundant edema on the paranasal sinuses.
How does Sinusitis Present?
Patients with sinusitis typically, women have more occurrences of infective sinusitis than men. Present at age range of 3 to 15years most common in children than adults. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sinusitis include. Nasal obstruction., mucopurulent nasal drainage, craniofacial discomfort described/interorbital heaviness such as facial dull pain, frank periorbital, or facial edema. fever (new-onset), cough that worsens at night, diminished sense of smell.
How is Sinusitis Diagnosed?
Sinusitis is diagnosed through the medical history and physical exam.
How is Sinusitis Treated?
Sinusitis is treated through the following modalities: Medical care – antimicrobial medication first line amoxicillin. Symptomatic treatment includes Warm compresses, adequate hydration, nonnarcotic analgesia, smoking cessation, humidification, and balanced nutrition.
What is the Prognosis of Sinusitis?
The prognosis of sinusitis is fair. Roughly about 40% case of acute sinusitis resolves impulsively without antibiotics. The impulsive cure of viral origin sinusitis is about 98%. When treated with proper antibiotics, show speedy improvement. The relapse rate after efficacious treatment is <5%.