Sjögren syndrome is a chronic disease associated with dry mouth (xerostomia) and dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca) due to immune destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands.
What is Sjögren Syndrome?
Sjögren syndrome an autoimmune disease that cause dysfunction in the exocrine glands.
What is the Pathology of Sjögren Syndrome?
The pathology of sjögren syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of sjögren syndrome is not well understood but can be linked to environmental or endogenous antigens that trigger self-acting inflammatory response.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sjögren syndrome starts with an infection or any process that can trigger an immune response in susceptible individuals. This trigger leads to epithelial cell activation and leads to a prolonged inflammatory response that resembles features of systemic autoimmunity.
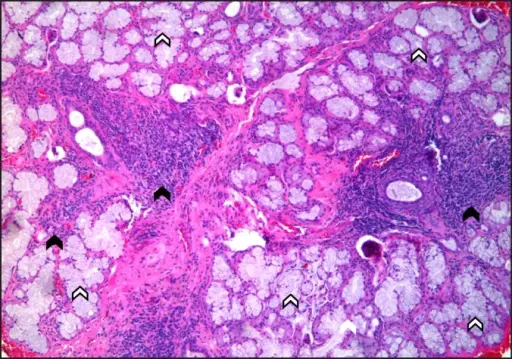
-Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with sjögren syndrome drying of corneal epithelium, inflammation, erosion, and ulceration of the epithelium; atrophy with inflammation, fissuring and ulceration of oral mucosa, drying and crusting of the nose that may lead to ulceration.
How does Sjögren Syndrome Present?
Patients with sjögren syndrome typically affects female more than males and can affect individuals at any age but manifests more often in the fourth to fifth decade of life, with median age of 53 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sjögren syndrome include dry eyes and dry mouth, parotitis, skin dryness, raynaud phenomenon. It can also affect other part of the body such as Lungs, Gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, heart, and the CNS.
How is Sjögren Syndrome Diagnosed?
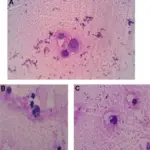
Sjögren syndrome is diagnosed through laboratory findings of elevated ESR, Presence of ANA, RF, and anti-alpha-fodrin antibody; leukopenia, anemia. Eosinophilia, and hypergammaglobulinemia. Schirmer test, staining, salivary testing, and protein profiling can also be utilized.
How is Sjögren Syndrome Treated?
Sjögren syndrome is treated based on the patient’s symptoms. Creams for dryness, NSAIDs for arthralgia’s; steroids, and immunosuppressive drugs can also be used for lymphocytic lung disease.
What is the Prognosis of Sjögren Syndrome?
The prognosis of sjögren syndrome is generally good, and mostly depends on the associated disorder.