Skeletal syphilis or osseous syphilis bony involvement by Treponema pallidum.
What is the Pathology of Skeletal Syphilis?
The pathology of skeletal syphilis is:
-Etiology: The cause of skeletal syphilis is bacterium treponema pallidum
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to skeletal syphilis involves a tiny organism called treponema.
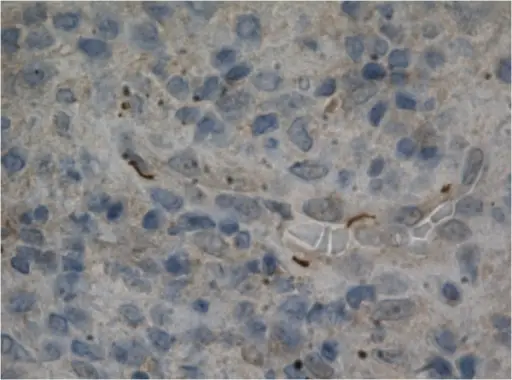
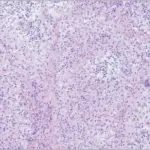
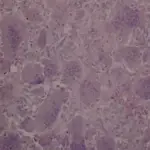
-Histology: The histology associated with skeletal syphilis shows interstitial inflammation, endothelial swelling, irregular acanthosis, elongated rete ridges, a vacuolar pattern with lymphocytic infiltration.
How does Skeletal Syphilis Present?
Patients with skeletal syphilis typically affect males 20-50 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with skeletal syphilis include periostitis, osteitis, osteomyelitis, and osteolysis.
How is Skeletal Syphilis Diagnosed?
Skeletal syphilis is diagnosed by dark-field microscopy and serological tests.
How is Skeletal Syphilis Treated?
Skeletal syphilis is treated by penicillin which is the drug of choice.
What is the Prognosis of Skeletal Syphilis?
The prognosis of skeletal syphilis is variable.