Spitz nevus is a skin lesion that mostly affects children and the young generation.
What is the Pathology of Spitz Nevus?
The pathology of the study of skin disease with the aim to identify the cause of the pathology and the histology of the disease.
-Etiology: The cause of spitz nevus is currently unknown.
-Genes involved: BAP1 and BRAF.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to spitz nevus is melanoocytic proliferation.
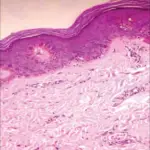
-Morphology: The morphology associated with spitz nevus shows pigmented bands symmetrically spread at the lesion margin.
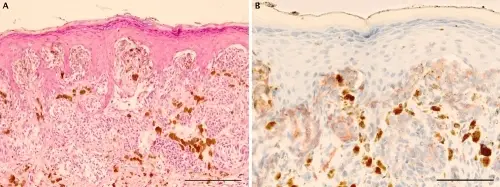
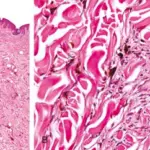
-Histology: The histology associated with spitz nevus shows nests containing spindle-shaped and epithelioid cells. Have abundant cytoplasm with conspicuous nucleoli.
How does Spitz Nevus Present?
Patients with spitz nevus are typically more female than the male with a mean age of 22 years and mostly in the lower extremity. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with spitz nevus include solitary symmetrical well-circumscribed, pink pigmented dome-shaped papule.
How is Spitz Nevus Diagnosed?
The spitz nevus is diagnosed by physical examination and by the use of a dermatoscope.
How is Spitz Nevus Treated?
The spitz nevus is treated by surgical removal or excision but the doctors recommends frequent monitoring before removal.
What is the Prognosis of Spitz Nevus?
The prognosis of spitz nevus is good. His is because the lesion is mostly benign.