Splenic marginal zone lymphoma is a low-grade B-cell lymphoma that is unique to the spleen but that often secondarily involves the splenic hilar lymph nodes and usually involves the blood and bone marrow.
What is the Pathology of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma?
The pathology of splenic marginal zone lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of splenic marginal zone lymphoma is not known. It is more common in people who have been infected with hepatitis C virus and some autoimmune conditions.
-Genes involved: TP53 gene, NOTCH2 gene, KLF2 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to splenic marginal zone lymphoma involves antigen or superantigen stimulation and molecular deregulation of different genes (including NOTCH2 and KLF2) involved in normal lymphocyte differentiation.
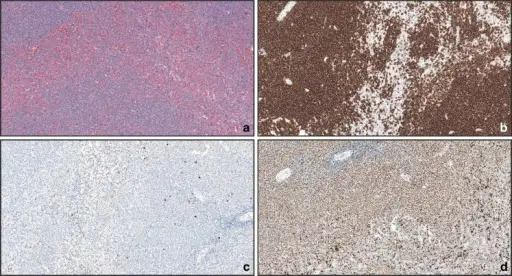
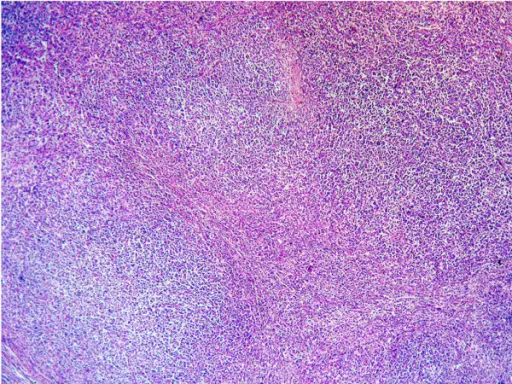
-Histology: The histology associated with splenic marginal zone lymphoma shows prominent expansion of the white pulp by small lymphocytes that often replace the normal germinal centers and efface the normal mantle zones.
How does Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Present?
Patients with splenic marginal zone lymphoma typically have equal distribution between males and females, present at age range of 65-70 years. The median age at diagnosis is 65 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with splenic marginal zone lymphoma include moderate to massive splenomegaly, autoimmune anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia which could be attributed to bone marrow infiltration and splenic sequestration. The majority of the patients show absolute lymphocytosis.
How is Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Diagnosed?
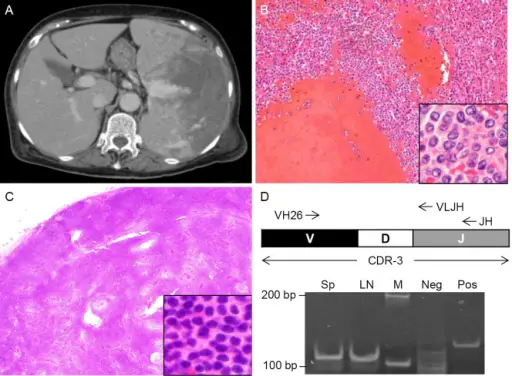
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma is diagnosed by spleen histology; if that is not available, diagnosis requires integration of bone marrow histology with cell morphology and immunophenotype in the blood and bone marrow.
How is Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Treated?
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma is treated by splenectomy or splenic radiation, chemotherapy and targeted antibody therapy with rituximab.
What is the Prognosis of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma?
The prognosis of splenic marginal zone lymphoma is fair. The median survival is approximately 8 to 10 years.