Staphylococcal bacterial infection is caused by staphylococcus bacteria commonly found on the skin or in the nose of even healthy individuals.
What is the Pathology of Staphylococcal Bacterial Infection?
The pathology of staphylococcal bacterial infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of staphylococcal bacterial infection is staphylococcus bacteria.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to staphylococcal bacterial infection are when S. aureus inoculates into an open wound, and upon contact with mucosal surface it upregulates the virulence genes which cause the activation of the immune system.
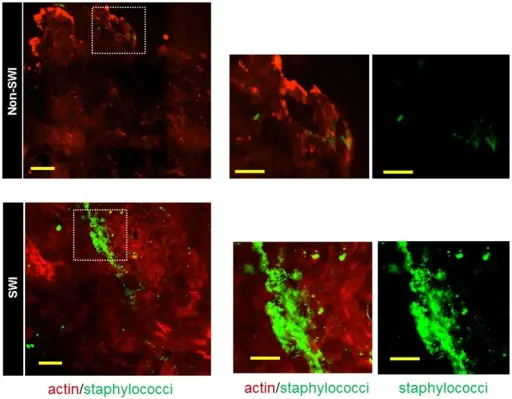
-Morphology: The morphology associated with staphylococcal bacterial infection shows gram-positive, non spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, nonmotile, catalase-positive or negative, small, spherical bacteria from pairs to, and grape-like clusters.
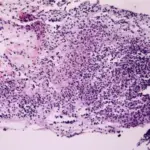
-Histology: The histology associated with staphylococcal bacterial infection shows gram positive cocci in clusters.
How does Staphylococcal Bacterial Infection Present?
Patients with staphylococcal bacterial infection typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with staphylococcal bacterial infection include sore, red eyelids or eyes, and painful red lump or bump on the skin.
How is Staphylococcal Bacterial Infection Diagnosed?
Staphylococcal bacterial infection is diagnosed by echocardiogram, tissue sample or nasal secretions.
How is Staphylococcal Bacterial Infection Treated?
Staphylococcal bacterial infection is treated by antibiotics and drainage of the infected area.
What is the Prognosis of Staphylococcal Bacterial Infection?
The prognosis of staphylococcal bacterial infection is fair. When these infections are left untreated, they can lead to organ failure and death.