Streptococcal bacterial infection is any type of infection caused by the group of bacteria.
What is the Pathology of Streptococcal Bacterial Infection?
The pathology of streptococcal bacterial infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of streptococcal bacterial infection is Streptococcus.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
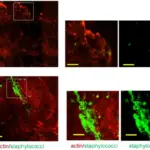
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to streptococcal bacterial infection the bacteria enters and colonizes the upper respiratory tract and invades epithelial cells, where it produces toxins which are responsible for host cell damage and inflammatory response.
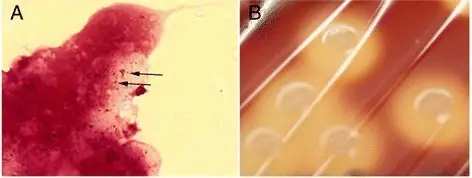
-Morphology: The morphology associated with streptococcal bacterial infection shows gram-positive cocci in chains or clusters.
-Histology: The histology associated with streptococcal bacterial infection shows inflammation with polymorph neutrophil infiltration, cytotoxic effects, and necrosis.
How does Streptococcal Bacterial Infection Present?
Patients with streptococcal bacterial infection typically are all genders of all age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with streptococcal bacterial infection include fever, headache, tender lymph nodes, and pain with swallowing.
How is Streptococcal Bacterial Infection Diagnosed?
Streptococcal bacterial infection is diagnosed by swab test.
How is Streptococcal Bacterial Infection Treated?
Streptococcal bacterial infection is treated by medications such as penicillin and amoxicillin.
What is the Prognosis of Streptococcal Bacterial Infection?
The prognosis of streptococcal bacterial infection is fair. An untreated infection with a pus-filled discharge can remain infectious for months.