Stromal hyperthecosis are presence of nests of luteinized theca cells in the ovarian stroma due to differentiation of the ovarian interstitial cells into steroidogenically active luteinized stromal cells.
What is the Pathology of Stromal Hyperthecosis?
The pathology of stromal hyperthecosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of stromal hyperthecosis is unknown. However, it may be due to genetic transmission.
-Genes involved: CDH1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to stromal hyperthecosis is unknown.
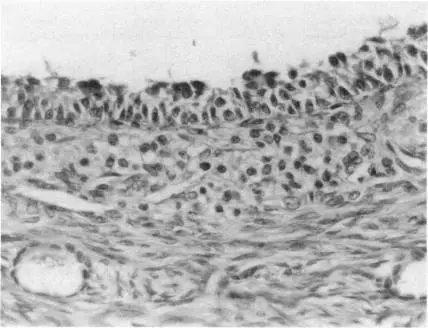
-Morphology: The morphology associated with stromal hyperthecosis shows uniform enlargement of both ovaries,
-Histology: The histology associated with stromal hyperthecosis shows scattered nests of luteinized theca cells
How does Stromal Hyperthecosis Present?
Patients with stromal hyperthecosis typically females in 60-70 years age and less common in reproductive age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with stromal hyperthecosis include: slowly progressive acne, hirsutism, virilization, obesity with striking virilization and insulin resistance.
How is Stromal Hyperthecosis Diagnosed?
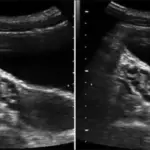
Stromal hyperthecosis is diagnosed by histological examination of ovaries, sonography.
How is Stromal Hyperthecosis Treated?
Stromal hyperthecosis is treated by: antiandrogen therapy, Possibly excision, leuprolide if poor surgical candidate.
What is the Prognosis of Stromal Hyperthecosis?
The prognosis of stromal hyperthecosis is good. However an increased risk for metabolic complications of hyperlipidemia and type 2 diabetes is there.