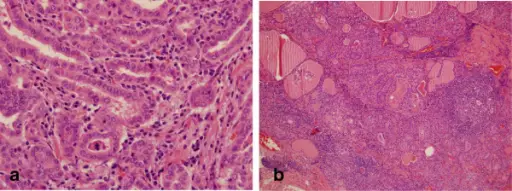
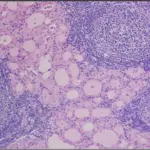
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is the Inflammation of the thyroid gland that includes granulomas.
What is the Pathology of Subacute Lymphocytic Thyroiditis?
The pathology of subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is:
-Etiology: The cause of subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is a systemic viral infection.
-Genes involved: HLA-B35.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis includes the destruction of follicular epithelium and loss of follicular integrity.
-Histology: The histology associated with subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis shows neutrophils and destruction of follicles with colloid depletion in early cases and fibrosis in late cases.
How does Subacute Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Present?
Patients with subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis are typically middle aged females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis include myalgia, fatigue, prostration, high-grade fever, malaise, dysphagia, hoarseness, and pain over the thyroid area.
How is Subacute Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Diagnosed?
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is diagnosed using a radioactive iodine uptake test (RAIU).
How is Subacute Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Treated?
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is treated with aspirin, prednisone, and propranolol.
What is the Prognosis of Subacute Lymphocytic Thyroiditis?
The prognosis of subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is very good as the symptom reversed in 1-3 months.