Sudden cardiac death is an unexpected death due to loss of cardiac function within 1 hour of symptom onset.
What is the Pathology of Sudden Cardiac Death?
Sudden cardiac death pathology is associated with coronary artery occlusion, aneurysm, rupture, dissection, spasm, arteritis, and coronary anomalies of vessels.
How does Sudden Cardiac Death Present?
Sudden cardiac death has a prodrome of chest pain, fatigue, palpitations, and other nonspecific complaints.
How is Sudden Cardiac Death Diagnosed?
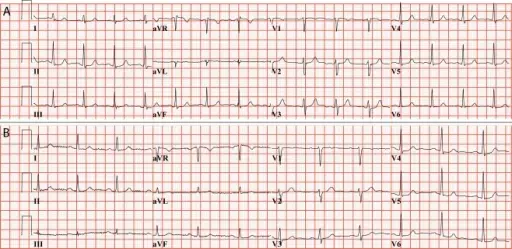
Sudden cardiac death diagnosis includes laboratory studies of cardiac enzymes, electrolytes, calcium, magnesium, BNP, and inflammation markers. For imaging, 2D echo, chest x-ray, and electrocardiogram are utilized.
How is Sudden Cardiac Death Treated?
Sudden cardiac death is treated with intensive monitoring; resuscitative efforts may be conducted. For drug therapy, beta blockers, and anti-arrhythmic drugs may be given. ICD placement may be used for prevention as well as temporary cardiac pacing, radiofrequency ablation, cardioverter defibrillator therapy and surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Sudden Cardiac Death?
Sudden cardiac death prognosis is poor with >40% unwitnessed deaths each year. Surviving patients have a recurrence rate of 20%.