Syphilis is a disease caused by Treponema pallidum.
What is the Pathology of Syphilis?
The pathology of syphilis is:
-Etiology: The cause of syphilis is a spirochete organism called treponema pallidum.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to syphilis is when treponema pallidum enters an individual byby sexual contact, and penetrate through intact mucous membrane and invade the blood stream, enters other body parts causing the progressive tissue destruction.
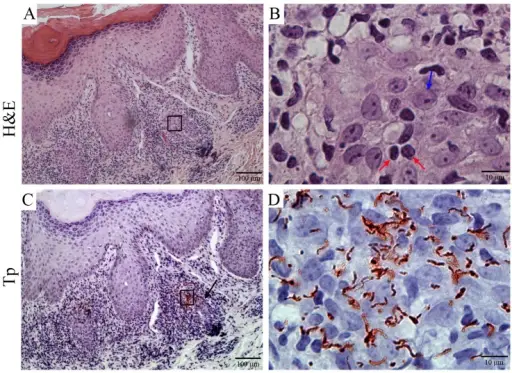
-Morphology: The morphology associated with treponema pallidum shows a two-layered outer wall, a cytoplasmic membrane proper, cytoplasm and a bunch of fibrils following a different path in different places on the treponema.
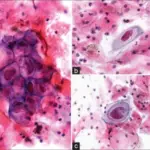
-Histology: The histology associated with treponema pallidum shows papulosquamous thin papules, rash, moth-eaten alopecia and coiled spirochetes.
How does Syphilis Present?
Patients with syphilis typically are all genders at the age range of 25–34 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with treponema pallidum include weight loss, muscle aches, fatigue, fever, swollen lymph glands.
How is Syphilis Diagnosed?
Syphilis is diagnosed by PCR, and blood test.
How is Syphilis Treated?
Syphilis is treated by antibiotics such as benzathine penicillin
What is the Prognosis of Syphilis
The prognosis of treponema pallidum is good if it does not enter the body organs. Antibiotics can cure the infection, but there’s no way to repair organs that have been damaged by syphilis.