Systemic sclerosis, also called scleroderma, is an autoimmune condition in which certain tissues become fibrotic, especially small blood vessels and skin.
What is Systemic Sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis is a systemic connective tissue disease that that affects the skin, joints, and internal organs.
What is the Pathology of Systemic Sclerosis?
The pathology of systemic sclerosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of systemic sclerosis is attributed to environmental exposures to silica,. Organic solvents, alipathic hydrocarbons, epoxy resin, and pesticides as well as use of appetite suppressants, substances in cosmetic procedures, and vibration injury.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to systemic sclerosis is the exposure to environmental factors that leads to vascular and immunologic dysfunction resulting to fibrosis and obliterative vasculopathy.
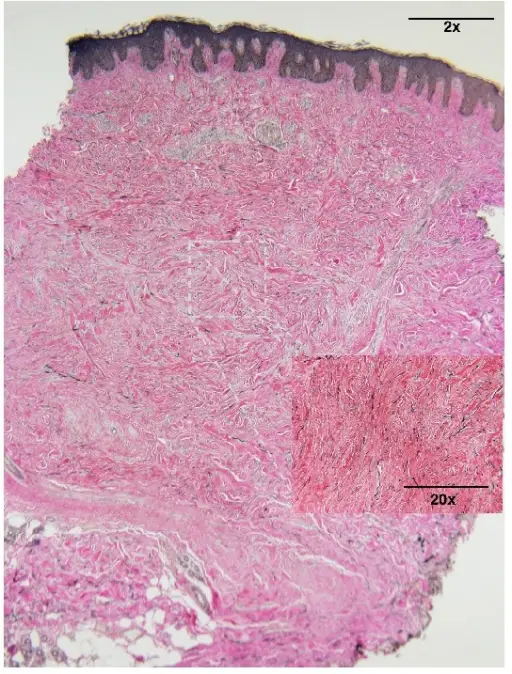
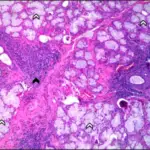
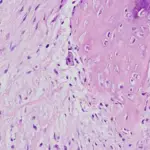
-Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with systemic sclerosis are severe fibroproliferative vascular lesion of small arteries and arterioles, excessive deposition of collagen in skin and internal organs.
How does Systemic Sclerosis Present?
Patients with systemic sclerosis are typically women more than men with a 10:1 ratio. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with systemic sclerosis include cutaneous pruritus, raynaud phenomenon, dysphagia and GIT symptoms, shortness of breath on exertion, joint pain, and weakness.
How is Systemic Sclerosis Diagnosed?
Systemic sclerosis is diagnosed through findings from laboratory studies such as an increases ESR, creatinine phosphokinase levels, and urea and creatinine levels. Hypergammaglobulinemia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and C-reactive protein may also be helpful. Imaging and lung function tests are used to assess severity and degree of involvement of other areas of the body.
How is Systemic Sclerosis Treated?
Systemic sclerosis is treated based on presentation of the disease. For Raynaud phenomenon and ulcer manifestation, calcium channel blockers, prostanoids, tadalafil, and bosentan are recommennded. For pruritus, Camphor and menthol, topical emollients, Psoralen UV-A (PUVA) treatment, and UVA-1 phototherapy may be helpful. In calcinosis, surgery is advised.
What is the Prognosis of Systemic Sclerosis?
The prognosis of systemic sclerosis is dependent on the type of sclerosis present in the patient. Diffuse systemic sclerosis, compared with limited systemic sclerosis, can lead to death if not treated promptly. The presence of pulmonary hypertension is also a significant factor in survival.