Tenosynovial giant cell tumors are a group of rare, benign tumors that involve bursae, synovium, and tendon sheath.
What is the Pathology of Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor?
The pathology of tenosynovial giant cell tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of tenosynovial giant cell tumor is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to tenosynovial giant cell tumors is unknown.
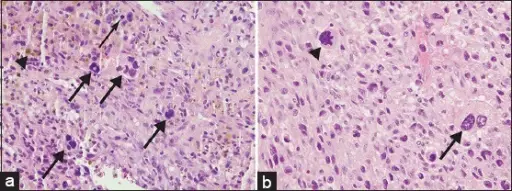
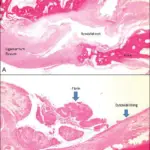
-Histology: The histology associated with tenosynovial giant cell tumors shows mononuclear stromal cells with small round nuclei.
How does Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor Present?
Patients with tenosynovial giant cell tumors are males or females typically between 25 and 40 years old. The signs and symptoms of tenosynovial giant cell tumors vary depending upon the location, but tend to include swelling.
How is Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor Diagnosed?
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is diagnosed using X-ray and MRI.
How is Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor Treated?
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is treated using surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor?
The prognosis of tenosynovial giant cell tumors is fair.