Tetralogy of fallot is one of the most common congenital heart problems that consist of heart defects that impede normal blood flow in the heart.
What is the Pathology of Tetralogy of Fallot?
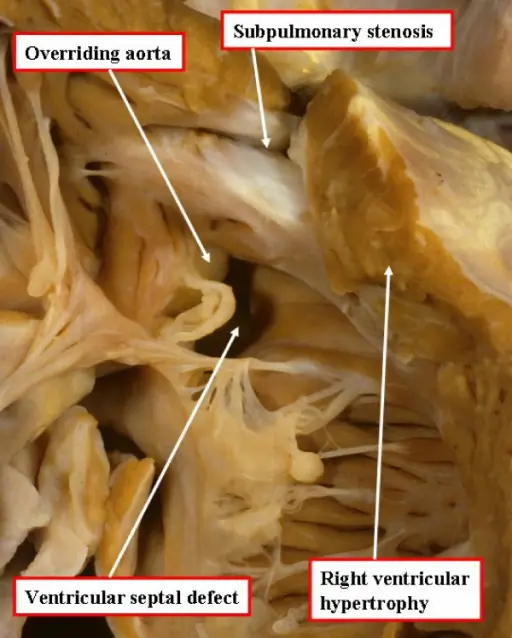
Tetralogy of fallot consists of ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, a misplaced aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
How does Tetralogy of Fallot Present?
Tetralogy of fallot is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease. It presents as failure to thrive in infants, with cyanosis if it occurs with pulmonary atresia. Tet spells may be observed in infants in which their skin turns blue when they feed or cry.
How is Tetralogy of Fallot Diagnosed?
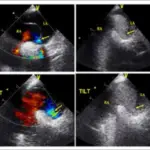
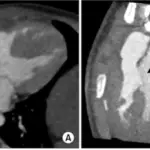
Tetralogy of fallot is diagnosed with laboratory studies such as CBC, coagulation studies, arterial blood gas and blood cultures. For imaging, the following may be utilized: chest x-ray (boot-shaped heart), 2D echo and MRI. Squatting in older children produces a compensatory mechanism that increases peripheral vascular resistance and reduces the extent of right-to-left shunt.
How is Tetralogy of Fallot Treated?
Tetralogy of fallot treatment is mostly surgical with pulmonary valve replacement most commonly performed in adults.
What is the Prognosis of Tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of fallot prognosis is excellent with treatment, but for the untreated, mortality rate is at 50% by the age of 6 years old.