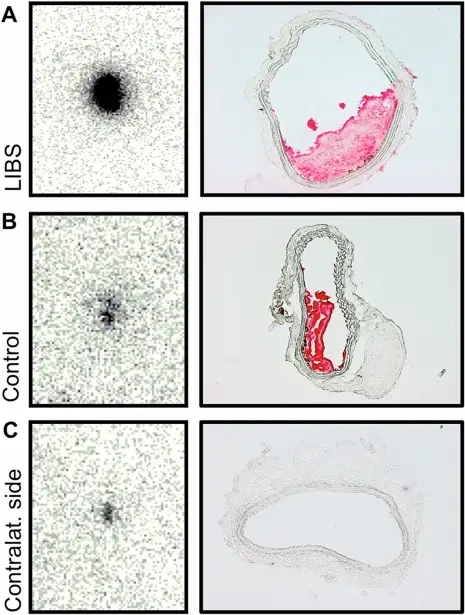
Ex vivo autoradiography of carotid artery thrombosis.Ex vivo autoradiography of carotid artery specimens (left column) and appendent transversal histology sections of carotid arteries immunohistochemically stained for CD41 (right column). Autoradiography of the injured carotid artery, after treatment with ferric chloride, reveals a strong ligand uptake after incubation with 111In-LIBS (A). Corresponding histology proves the presence of a non-occlusive wall-adherent thrombosis. After incubation with 111In-control, the radioligand uptake appears visually decreased (B). Autoradiography of the carotid artery on the contralateral non-injured side allowed the assessment of background radiation in the absence of an intravascular thrombosis (C). Activated platelets in carotid artery thrombosis in mice can be selectively targeted with a radiolabeled single-chain antibody. Heidt T, Deininger F, Peter K, Goldschmidt J, Pethe A, Hagemeyer CE, Neudorfer I, Zirlik A, Weber WA, Bode C, Meyer PT, Behe M, von Zur Mühlen C - PloS one (2011). Not Altered. CC.
Thrombosis is a blood clot within a vessel.
There are two main types of thrombosis:
- Venous thrombosis: Blood clot blocks a vein.
- Arterial thrombosis: Blood clot blocks an artery.
