Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel. It prevents blood from flowing normally through the circulatory system.
What is the Pathology of Thrombosis?
The pathology of thrombosis is:
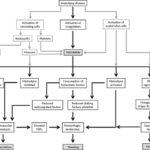
-Etiology: The cause of thrombosis is Virchow’s triad issues.
-Genes involved: Certain clotting factors may be implicated.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to thrombosis formation begins when platelets bind to collagen exposed at the site of vascular injury. Such binding leads to platelet activation, as a result of which platelet membranes acquire the ability to provide catalytic support for the biochemical reactions that lead to thrombin formation.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with thrombosis shows variable size and shape, may develop anywhere in the cardiovascular system, occurs in sites of stasis, firmly attached to the point of origin.
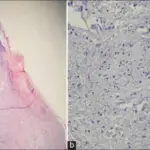
-Histology: The histology associated with thrombosis shows attachment to the vessel wall, and Lines of Zahn.
How does Thrombosis Present?
Patients with thrombosis typically affect males present at the age range of 40 and above, mostly in advanced age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with thrombosis include warm skin around the painful area, throbbing or cramping pain most common location is the deep veins (DVT) of the leg below the knee, which can occur in an artery or vein, swollen veins that are hard or sore when you touch them, warm skin around the area.
How is Thrombosis Diagnosed?
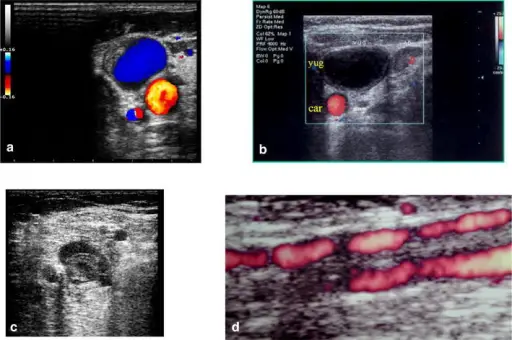
Thrombosis is diagnosed using blood tests, ultrasound, venography, CT scan, and MRI.
How is Thrombosis Treated?
Thrombosis is treated with anticoagulants, catheters, stents.
What is the Prognosis of Thrombosis?
The prognosis of thrombosis is good and resolves completely with no complication.