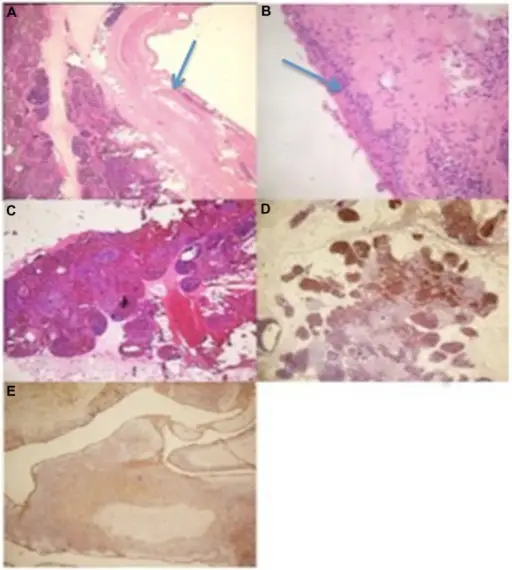
(A) The coexistence of a cystic lesion (arrow) and true thymic hyperplasia (hematoxylin and eosin stain [HE] ×250; (B) the epithelial lining (arrow) of the cyst was mainly flattened and focally hyperplastic (HE ×400); (C) true thymic hyperplasia is characterized by the conservation of the thymic architecture which consists of a corticomedullary differentiation and the presence of many Hassall’s corpuscles in the medulla (HE ×250); (D) immunohistochemical study showing the positivity of the lymphocytes with the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase antibody (HE ×250); (E) immunohistochemical study showing the positivity of the epithelial lining with the cytokeratin antibody (HE ×250). A unilocular thymic cyst associated with true thymic hyperplasia: a challenging diagnosis especially in a child: Mlika M, Gattoufi W, Zribi H, Braham E, Marghli A, El Mezni F - International medical case reports journal (2015). Not altered. CC.
The term thymic hyperplasia is an inaccurate term.
Although it is referred to as “thymic hyperplasia”, thymic hyperplasia is actually due to thymic follicular hyperplasia.
Thymic hyperplasia may be seen in autoimmune conditions such as, graves disease, lupus erythematous, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis.